The global sewing industry brought in over $9 million in 2022. As people become more interested in sustainability and buying handmade, unique pieces, the demand for custom sewing continues rising. Sewing skills allow creative entrepreneurs to start their own sewing business making clothes, crafts, accessories, home goods, and more.
Whether selling online through Etsy or at local craft fairs, small business owners can tap into this expanding market. With some basic equipment, skills, and dedicated time for sewing and promotion, this accessible business allows budding entrepreneurs to monetize their creativity.
This guide will walk you through how to start a sewing business. Topics include sourcing materials for sewing projects, market research, competitive analysis, registering an EIN, forming an LLC, obtaining business insurance, and other important details.
1. Conduct Sewing Market Research
Market research is essential to starting a professional or home based sewing business. It offers insight into your target market, trends in services and sewing products, the largest competitors in your area, and more details to help form a thorough business plan.
Some details you might learn through sewing services market research include:
- The sewing tools and services market is ripe for new sewing businesses focused on made-to-order and customized products.
- Selling projects online through sewing hobby platforms like Etsy has strong potential.
- Specializing in a niche category within the market can help budding businesses stand out.
- Older artisans near retirement age dominate quilting.
- The average annual spending on quilting and sewing supplies is $489 per customer, showing substantial opportunities to capture spending from a dedicated demographic.
- Offering beginner quilting classes can further differentiate a small quilting business.
- For apparel and accessory makers, sustainability is key.
- Roughly 90% of Gen Z look for eco-friendly attributes when shopping.
- Specializing in upcycled designs or zero-waste patterns provides a competitive edge.
New sewing businesses can find a loyal customer base by identifying a profitable niche with distinctive offerings. The low startup costs relative to potential sales make this a compelling opportunity for budding entrepreneurs.
2. Analyze the Competition
Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for any new business, including sewing. Begin by identifying local sewing, alterations, and craft businesses around you and online. Whether you’re a home sewing business or a commercial operation, knowing about other local businesses helps you get ahead.
Some other ways to get to know local small business competitors in the sewing industry include:
- While a new sewing business likely won’t directly compete with established retailers, this competitor research shows customer demand and spending in the area.
- Search Etsy and online craft marketplaces by product category and location.
- Filter by bestselling items and read full shop profiles of top competitors, noting years in business, products offered, policies, reviews, and sales volume.
- Analyzing competitors’ photography, descriptions, and shop branding also inspires.
- Evaluating competitors’ social media and web presence is equally important.
- Perform Google searches to uncover active sewing blogs, YouTube channels, and Instagram business profiles with engaged followers in the target customer demographic.
- Compare content and followings to find leaders establishing authority and expertise.
- Examining the Facebook groups and Pinterest boards sewing customers follow can further reveal influencers and styles inspiring purchases.
While fewer direct competitors than retailers, monitoring content from sewing influencers allows new businesses to identify trending styles and techniques within sewing niches. Coupling insights from local brick-and-mortar analysis and broader online competitor evaluation helps tailor product offerings and branding to find a profitable, differentiated e-commerce niche.
3. Costs to Start a Sewing Business
When starting a sewing business, initial investments vary widely based on scale and offerings but expect roughly $10,000-$15,000 in start-up costs. Handmade product sellers and custom sewing service providers have lower initial investments than full manufacturing operations or retail boutiques.
Start-up Costs
Sewing Equipment – Expect to invest $2,000-$5,000 in commercial sewing/embroidery machines like:
- Basic Sewing Machine – $500-$2,000
- Computerized Machine – $3,000
- Embroidery Machine – $7,000-$10,000
Additional equipment like dress forms, irons, cutters, needles, storage, lighting, chairs, tables, shelves, etc. can cost a few thousand more. Leasing specialty equipment can reduce initial purchases.
Fabric, notions, threads, buttons, labels, and packaging for made-to-order start around $1,000. Wholesale supply vendors offer bulk discounts.
Ongoing Costs
Rent, insurance, accounting, equipment leasing, and other professional services drive recurring costs. While costs fluctuate based on sales and scale, dedicate 20-30% of ongoing gross sales to operating expenses.
- Dedicated Space – Home-based online sellers need a spare room or basement section costing a little upfront, while leased retail space or workshop builds ongoing rent expenses of $15-$30 per square foot monthly. Evaluate zoning regulations for commercial work from a residence.
- Licenses, Permits & Insurance – Registration fees, sales tax IDs, and business licenses average under $100 total, but special use or manufacturing permits add several hundred dollars in some areas. Liability insurance ranges from $500-$2,000 annually.
- Professional Services – Hiring a lawyer for contract review or a bookkeeper for taxes and accounting costs around $200 and $100 monthly, respectively. Website development, branding, and marketing designers cost between $500-$5,000 initially.
Once launched, revisit costs annually and expect around 50% of gross sales to cover ongoing fabric and materials. Staffing needs with contract workers or employees will become the primary monthly expense, ranging from $15-$25 hourly per sewer plus additional percent commissions on sales.
4. Form a Legal Business Entity
When establishing any small business, choosing the right legal structure significantly impacts taxes, liability protection, and ease of formation. Weighing the pros and cons of each for a sewing entrepreneur’s specific goals and scale is crucial.
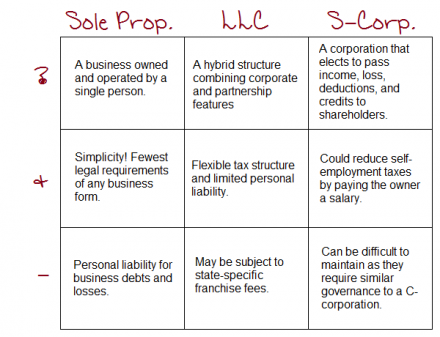
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship has the lowest start-up costs since it is not an official legal entity separate from the owner. It allows a sewing business owner to quickly start selling products or services under their name alone, directly reporting all profits and losses on personal annual tax filings with no corporate formalities to maintain.
Partnership
Forming a general or limited partnership allows multiple owners to combine investment and resources in a sewing business, governed by a formal written agreement outlining profit/loss distributions and partner roles. General partners have equal management rights but face the same unlimited liability as sole proprietors.
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
For the greatest liability protection, sewing business owners should establish limited liability companies (LLCs) by filing articles of organization with state agencies. LLCs limit financial liability to each owner’s investment and allow “pass-through” income tax treatment without needing to issue stock shares or maintain corporate minutes. Owners have flexibility in structuring operational agreements and adding investors through membership units.
Corporation
A more complex corporation offers the strongest liability shielding to owners but faces double taxation and extensive recordkeeping. Unless a sewing business plans to eventually pursue public fundraising through issuing stock shares, an LLC provides the most logical choice for small creative firms to protect personal assets if sued. Consult an attorney to select the optimal structure.
5. Register Your Business For Taxes
Unless operating as a sole proprietor using a Social Security Number for tax purposes, all sewing businesses should obtain free Employer Identification Numbers (EINs) from the IRS for federal tax filing and banking needs:
The online application takes under 10 minutes to complete. The IRS immediately issues EIN confirmation letters after answering basic questions on the proposed business structure.
To apply, first determine the sewing business’s legal structure: LLC, partnership, corporation, etc. Next, identify if you already file taxes using an SSN or existing EIN. Then, enter the number of employees or if hiring contractors. Finally, provide basic contact information and specify why the EIN is needed (bank account, federal taxes, hiring employees, etc.).
Once submitted, record the provided EIN for tax filings and bank account applications. This unique identifier allows small sewing businesses to open business bank accounts, apply for financing and formally register with state and federal tax agencies.
Additionally, visit your state revenue department website to obtain sales tax permit IDs for collecting and remitting sales taxes. For example, Arizona Transaction Privilege Tax Licenses cost $50 initially, then $20 annually. California Seller’s Permits are free. Reporting sales tax keeps sewing businesses legally compliant as they scale.
Between free EIN applications and nominal state registration costs, formally registering a sewing business establishes credibility with limited financial barriers. Sticking to required filing and reporting deadlines maintains valid registrations to legally operate. Once established, the EIN designation stays with sewing businesses if relocating across state lines, allowing smooth continuation of operations.
6. Setup Your Accounting
Meticulous financial recordkeeping is essential for any small business, especially creative ventures like sewing that blend inventory purchasing, contractor payments, and sales income.
Accounting Software
Rather than manually tracking every transaction, sewing entrepreneurs should utilize accounting software like QuickBooks to automatically import, categorize, and reconcile bank payments and deposits. Plans start around $20 monthly.
Hire an Accountant
Pairing accounting software with an accountant who understands the sewing industry provides optimal financial oversight and tax preparation. A qualified accountant offers services like:
- Monthly bookkeeping – $200 monthly
- Sales tax filings – $75 quarterly
- Payroll administration – $250 monthly
- Year-end income tax prep – $500 annually
Keeping these things organized ensures reliability and accountability where income is concerned.
Open a Business Bank Account and Credit Card
Sewing ventures should open dedicated business bank accounts and credit cards solely for company finances instead of mingling with personal spending. A separate business account facilitates accounting documentation and helps build credit history. Banks determine approved business card limits based on annual revenue and time in business.
7. Obtain Licenses and Permits
While sewing businesses have lower regulatory barriers than heavily licensed industries like food service or cannabis, acquiring proper credentials remains essential for legal compliance. Find federal license information through the U.S. Small Business Administration. The SBA also offers a local search tool for state and city requirements.
Common documentation includes:
- Business Licenses – Nearly all municipalities require annual business licenses with fees based on revenue. For example, Los Angeles charges $121+ annually while New York City licenses start at $75 with a $25 renewal. Seller’s permits may also be needed.
- Zoning Permits – Using residential properties for commercial activities requires zoning approval with home occupation permits. Fees range from $50-$500+ depending on the municipality. Violating zoning mandates risks fines.
- Health Inspections – On-site sewing instruction, fabric shops, and manufacturing workshops may need health and safety inspections, which average $150-$300 apiece. Maintaining clean, hazard-free public access spaces ensures certification.
- Seller’s Permits – While not universally required, over half of states mandate seller’s permits for sales tax collection. Low-cost permits must be renewed annually. California, for example, requires a one-time $70 fee. Neglecting mandated seller’s permits risks fines upwards of $1,000.
- Sales & Use Tax Licenses – If selling products through retail channels, collecting customer sales tax requires licensing at $10-$100+, renewed annually. The Streamlined Sales and Use Tax Agreement helps determine specific municipality collector filing designations.
- Insurance – General liability insurance protects sewing businesses financially from third-party bodily injury, property damage, personal injury, and advertising injury claims stemming from premises risks, completed operations, and products.
Acquiring necessary credentials before launch helps sewing ventures open doors smoothly, operate legally, and gain customer confidence. While permit requirements vary, consulting local municipalities, SBA offices, and business lawyers determines needs. Following proper protocols prevents stressful repercussions.
8. Get Business Insurance
Business insurance protects sewing ventures from unexpected liabilities that could permanently shutter operations. Policies cover expenses if sued, inventory is stolen or destroyed, or customers are injured on-site. Without coverage, owners assume full financial responsibility out-of-pocket.
Potential incidents include:
- A customer trips on a rug in a fabric shop, breaks an arm, and sues for medical bills and lost wages from missed work.
- An electrical fire sparked from a sewing machine destroys workshop inventory and equipment.
- A disgruntled former contractor steals proprietary sewing patterns and customer lists, requiring legal action.
After registering a formal business structure, owners can apply online through providers like Progressive, or other local insurance brokers. Expect to provide details on:
- Business type – LLC, sole proprietor, etc.
- Location(s), size, and assets
- Inventory value
- Public foot traffic
- Years in operation
- Past liability claims
Common starter policies cost $500-$1,500 annually for $500,000 to $3 million coverage including general liability, property damage, inventory, and professional coverage. Higher-risk businesses or claims histories increase premiums.
9. Create an Office Space
Whether coordinating remote contractors, meeting clients for custom fittings, or running daily administrative tasks, securing dedicated office space lends professionalism and productivity when growing a sewing business.
Home Offices
Home-based offices allow low overhead for pattern makers, online retailers, and sole proprietors. Dedicated home creative spaces run a little upfront but require household storage for materials. Working from home offers no commute, tax deductions for office supplies, and flexible hours. However, productivity can lag without separation between business and personal life.
Coworking Spaces
For sewing professionals seeking community, coworking spaces like WeWork provide open floor plans for $150-$500 monthly per desk. Coworking offers workplace amenities from conference rooms to coffee bars without overhead or leases. While inventory storage limits exist, creatives can network, host clients for fittings when needed, and maintain productivity among other entrepreneurs.
Commercial Offices
Sewing brands needing dedicated storefronts with large workrooms, private offices, and custom build-outs should expect $15-$30 per square foot monthly in leased commercial spaces. These large investments suit retailers planning warehousing, distribution, and showrooms more than online ventures.
10. Source Your Equipment
Launching a sewing brand requires key equipment like industrial machines, tools, and notions, available through new purchases, used deals, rentals, and leasing options. Savvy entrepreneurs comparison shop across platforms as they build inventories scaled to current workloads.
New Equipment
New commercial machines, notions, accessories, and tools are purchasable through retailers like local dealers, Amazon, online specialty shops, and big box craft stores. Investing in warrantied equipment from reputable dealers like Singer builds long-term foundations for consistent quality. However new equipment carries higher price tags – commercial machines range $5,000+ – straining slim startup budgets.
Used Equipment
Sites like Craigslist, Facebook Marketplace, and NextDoor frequently list quality refurbished sewing machines under $2,000 from dealers and at-home sewists upgrading equipment. Joining local sewing groups and checking resale listings can uncover commercial machines and notions at half-retail prices to divert savings toward business growth.
Rentals
Sewing machine companies and specialty retailers like Sewing Machines Plus offer short or long-term rentals for commercial equipment, providing temporary solutions before investing in purchasing. However, accumulating monthly rental fees can soon eclipse buying costs outright. Consider projected sewing volumes before opting to continually rent instead of buying equipment.
Leasing
Equipment leases through companies like Marlin Leasing allow $0 down financing on commercial gear, structured into 12-60 month payment plans. While leasing facilitates access to advanced tools without major capital outlays, lengthy commitments carry interest charges affecting long-term costs.
11. Establish Your Brand Assets
Distinct branding conveys professionalism and memorability when introducing a new sewing brand, helping ventures stand out in competitive markets. From logos to websites, cohesive visual identity makes first impressions count.
Business Phone Lines
Calls build customer trust and projections of reliability over email alone. Services like RingCentral provide toll-free, local, or vanity 800 numbers from $30 monthly with easy setup. Portable forwarding routes calls across devices.
Logos and Branding
A polished logo becomes the face of a business across channels. Clean iconography – like spools of thread or sewing machines – with modern script fonts convey creativity within the sewing sector. Sites like Looka offer DIY logo makers for $20 or custom designs for around $500.
Business Cards and Signage
For in-person client meetings, trade shows, and local promotions, essentials like 500 Vistaprint business cards start around $20. Window signage and interior directional also feature branding during store visits.
Domain Names
The domain serves as the digital business headquarters, for example, onlinecustomsewing [dot] com. Short memorable names without odd hyphenations improve professionalism. Domain registrars like Namecheap offer domains for around $9 annually.
Websites
While social accounts offer a quick presence, websites establish SEO authority and sales funnels. Robust sites like Wix and Squarespace cost $12-$49 monthly for secure hosting, analytics, and lead generation tools. For under $200 on Fiverr, freelancers can custom code sites aligned to brand style guides.
12. Join Associations and Groups
Tapping into local sewing networks, guilds, and trade groups builds industry connections for honing skills, staying atop trends and potentially securing sales partnerships.
Local Associations
Long-running regional sewing collectives like the Stitch ‘N Bitch offer both virtual and in-person learning nights, sales bazaars, and guest lectures from area designers. Checking for chapters through the American Sewing Guild also connects entrepreneurs with discounts on events and credentials. Early involvement plants seeds for future collaborations and referrals.
Local Meetups
Sites like Meetup spotlight casual peer groups for activities from machine repair clinics to sewing technique lessons within most major metros, searchable by interest. Joining a few complementary groups creates low-pressure networking pipelines while supporting community education. Sewing professionals can also list their specialty workshops to promote brands through value-driven gatherings.
Facebook Groups
Spanning beginners to industry veterans, Facebook Groups like Free Sewing Patterns to Download and Print, Sewing Tips, and niche channels around sewing masks, quilting, or historical costuming foster idea exchanges and partnerships. The low barrier of requesting access allows sewing ventures to tap collective crowdsourcing on everything from workflow tips to supplier recommendations.
13. How to Market a Sewing Business
Strategic marketing establishes visibility and invaluable word-of-mouth referrals for sewing ventures. While quality workmanship retains customers, intentional outreach builds new pipelines.
Personal Networking
Tap connections through existing social networks and offer 10-20% discounts to delighted clients referring new patrons. Small gestures incentivize organic endorsements.
Digital Marketing
- Run Google/Facebook PPC ads targeted locally by interest in sewing and DIY hobbies with special offers for site traffic.
- Launch Instagram and TikTok accounts showcasing finished pieces and behind-the-scenes production. Embed online store links and run occasional social contests.
- Start a YouTube channel with sewing tutorials from basics to advanced techniques. Optimized video SEO drives subscribers over time.
- Blog regularly with sewing advice and project inspiration while linking to custom order services.
- Send email newsletters with new product launches, sales events, and company updates to website visitors.
Traditional Marketing
- Design eye-catching flyers and distribute them at local craft fairs, fabric shops, and community centers.
- Take out ads in regional arts magazines and event programs aligned with target demographics.
- Sponsor community fundraisers with item donations for program recognition.
- Print large vehicle wraps for delivery vans to spark curiosity during local trips.
- Host open house events and factory tours showing behind-the-scenes production.
- Run radio spots on local NPR stations during arts/culture segments.
Gradual community saturation through print, digital, and grassroots channels nurtures organic growth for sewing brands as expertise becomes familiar until reaching regional influence and beyond.
14. Focus on the Customer
For sewing brands competing against mass retailers on uniqueness and personalization, customer service directly fuels word-of-mouth referrals and repeat sales. Rather than transactional interactions, intimate craftsmanship demands exceptional support.
Carefully documenting requirements during initial fittings prevents errors in translating customer visions into finished pieces. Seamstresses should listen attentively to desired silhouettes, fabric preferences, delivery timelines, and custom adjustment requests.
Following project completion, custom sewing businesses should follow up for candid feedback and offer complimentary alterations for imperfect fits. Small gestures to rectify issues satisfy patrons who then endorse brands for responsiveness.
Additionally, surprising occasional clients with free basic repairs like replacing broken zippers or torn seams on older items purchased from your business sparks smiles through going above standard expectations.
By forging genuine connections with each customer fueled by understanding precise needs, and then exceeding those experiences through reliable delivery, proactive fixes, and open dialogue, loyalty grows within a community poised to recommend the sewing business to new audiences.
