The global mobile app market is expected to be worth over $935 billion by 2023 as more businesses and consumers continue adopting mobile solutions. With over 204 billion mobile app downloads in 2019 alone and increased time spent in apps, it’s an opportune time to build a business in this industry.
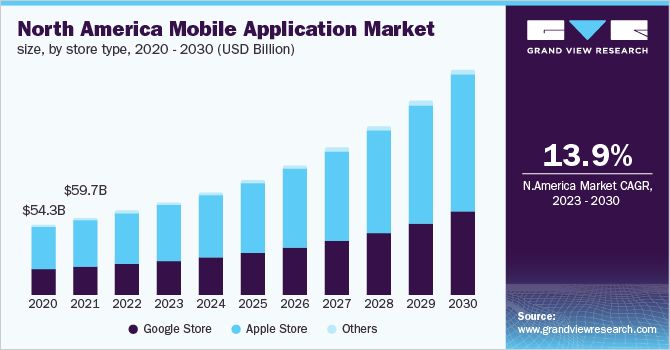
You can target various segments from gaming and entertainment apps to business and productivity solutions. Identify an audience need, develop a minimum viable product, and validate it before going to market. Refine based on user feedback for product-market fit.
This guide will walk you through how to start a mobile app business. Topics include market research, competitive analysis, registering your EIN, obtaining business insurance, marketing, customer outreach, and more.
1. Conduct Mobile App Market Research
Market research is essential to building a mobile app business plan. Market research offers insight into your target market, market saturation, and even where to launch your app, including the Google Play Store or the Apple App Store.
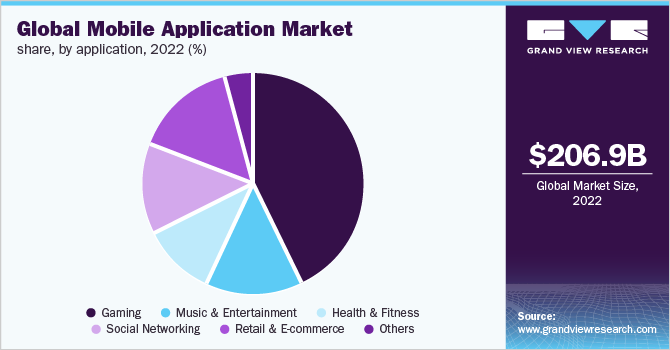
Some details you’ll learn through market research include:
- The average user has over 100 apps installed and uses around 30 of them each month.
- There are over 5 million apps across Android and iOS app stores.
- User acquisition costs remain relatively low compared to other channels.
- Cost per install can range from $0.10 to $2 for non-gaming apps. Mobile video games are also incredibly popular across both major platforms.
- There are various app monetization models including advertisements, in-app purchases, subscriptions, and transactions/bookings.
- Business models catering to productivity, communication, social networking, entertainment, and gaming are particularly lucrative.
- Apps focused on e-commerce, fintech, health & fitness tech, online learning, and remote work have seen strong growth.
- To build a large, sustainable app business, the key is to drive high user retention after the initial installs by delivering core value catered to user needs.
- User acquisition remains cost-efficient compared to other channels. Monetization potential is substantial.
With some strategic planning, persistence, and commitment to understanding evolving user needs, the environment is ideal for building an industry-leading, highly scalable, and profitable mobile app business right now.
2. Analyze the Competition
Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial before building your app. This guides development and marketing strategies.
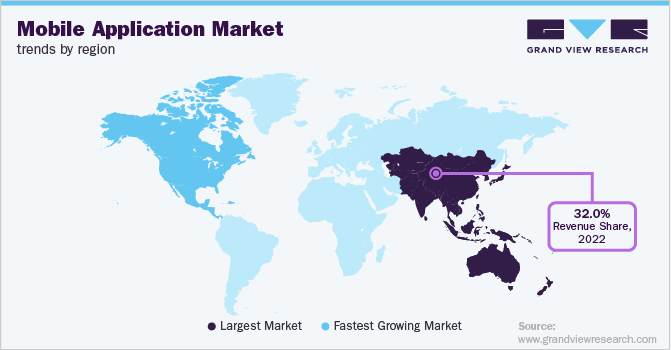
Some ways to research local Android app competitors include:
- Research existing apps in your target category on both Android and iOS stores. Analyze by several installs, ratings, reviews, and rankings.
- Study their user interface and user experience design. Sign up and thoroughly test features and functionality.
- Identify strengths, weaknesses, and differentiation opportunities.
- Check their public profiles to gauge traction like social media followers and engagement.
- See if they have raised any investments by searching press articles or platforms like Crunchbase.
- Search using keywords for their app name and category to find online reviews and discussions providing usage insights.
- Evaluate their go-to-market and growth strategy through app store listing optimization, social media, and online advertising campaigns.
- Assess effectiveness by installing their app through different channels.
- Research monetization models like subscriptions, in-app purchases, or ads.
- Study pricing page layouts and marketing copy effectiveness.
- Analyzing competition along these dimensions will reveal target users, their needs, and experience gaps to help position your app differently.
- It provides pricing guidance and sets customer expectation levels to deliver better value.
Ongoing evaluation even after launching your app is key to rapidly enhancing it based on the strengths competitors build while avoiding their weaknesses around negative reviews, low ratings, or stagnant installs. This market intelligence fuels product development and marketing priorities to sustainably gain market share.
3. Costs to Start a Mobile App Business
Launching native apps takes some startup capital. There are also ongoing costs associated with developing a successful app. Let’s break down mobile app development costs to better understand where your money goes.
Start-up Costs
- App Development – $50,000 to $250,000+ The complexity of your app and choice of developer will impact costs significantly. Basic apps with minimal functionality can be developed for as low as $50k. More complex apps with extensive features built on custom code can cost $250k+.
- Ongoing enhancements, new features, and fixes add more expense over time. Budget at least $25k annually for app maintenance and updates.
- High development costs upfront risk slowing progress if you run out of funds before launch. Consider an MVP first.
- Incorporation & Legal – $750 to $5000 Forming a legal business entity like an LLC provides liability protection. State filing fees are usually under $100 but legal services can cost $500 to $5000.
- Trademark registration for your business and app name can cost another $275 per registration. Complex partnerships may need extensive legal paperwork.
- Workspace Equipment & Software – $3000 to $15,000 desks, chairs, computers, and software for a small team of 2-5 employees can easily cost a few thousand dollars upfront. Cloud services and tooling add more annual expenses.
- Cloud Hosting & Web Services – $1000+ per year Hosting app servers, databases, storage and backups on scalable infrastructure like AWS can cost anywhere from a few hundred to thousands monthly depending on traffic and resources utilized.
Ongoing Costs
- Salaries – $5000+ per month Having at least a technical and marketing co-founder to build and launch the app is crucial. Later, grow your team in areas like design, engineering, analytics, customer support, etc. Average annual developer salaries range from $60k to $130k.
- Marketing & User Acquisition – $5000+ per month Paid user acquisition costs for mobile apps average $2-$4 per install. Budget at least $5k per month as you test channels and optimize conversions. Lifetime value must exceed the cost per install.
- Other fixed costs like office rent, payroll fees, and subscriptions can add up to thousands per month. Be frugal initially and focus directly on app development and user growth.
- Seek funding from angels, and VCs or apply for small business grants/loans if your savings cannot sustain at least 18-24 months of runway. Build traction before raising external capital.
Carefully projecting and tracking both fixed and variable costs from the start is vital to managing cash flows responsibly as you scale your app business.
4. Form a Legal Business Entity
To start a business launching your app, you must first form a legal business entity. There are four main business entities to choose from, including sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, and corporation.
Sole Proprietorship
Simplest structure with a single owner. There is no formal business registration unless you choose to register a DBA. The owner has unlimited personal liability for debts and lawsuits.
- Pros: No special tax considerations. Profits are passed directly to the owner to include on personal tax returns.
- Cons: Easy to form but high financial risk make sole proprietorships ill-suited for mobile app businesses that require major upfront tech investment and have liability risks around security, privacy, and intellectual property.
General Partnership
Similar to a sole proprietorship but with two or more owners. You can register as a formal partnership for clearer legal status and protections through a Partnership Agreement but this is optional.
- Pros: It still carries major unlimited personal liability. Partnerships can be complex to set up profits/losses sharing or making big business decisions.
- Cons: While convenient for early co-founders to collaborate, establishing an LLC or corporation is better suited as your mobile app startup begins hiring employees.
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
One of the most flexible structures that limits owner liability and combines pass-through taxation with limited personal liability protection for debts and legal judgments.
- Pros: Requires more formal state registration and paperwork plus adherence to strict LLC operating guidelines. But for the liability shield, administrative effort is well worth it for mobile app startups.
- Cons: As your app scales needing more complex operating agreements and ownership changes, forming a C-Corp or S-Corp later remains simpler compared to if you had started as a sole proprietorship or partnership initially.
Corporation (C-Corp or S-Corp)
Most complex and regulated structure but also offers the strongest owner protections and credibility for raising private/public investment needed for larger scale mobile apps.
- Pros: Corporate profits are taxed at both the corporate and personal levels. But an S-Corp election enables pass-through taxation while retaining corporate limited liability protections.
- Cons: Forming a corporation too early can mean excessive legal fees and administrative overhead that delay progress for early-stage mobile app startups. Starting as an LLC filing as an S-Corp later is simpler if needing external capital to grow.
5. Register Your Business For Taxes
An Employer Identification Number (EIN) is a unique nine-digit tax ID number assigned by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to business entities operating in the United States for tax filing and reporting purposes.
Unlike a Social Security Number which is tied to an individual, an EIN is specifically tied to your business structure like an LLC or Corporation.
Mobile app companies structured as sole proprietorships can use the owner’s SSN for federal tax purposes instead of an EIN but having an EIN adds credibility and makes your business entity distinct even as a solopreneur.
And if you plan to take on employees or contractors down the line, obtaining an EIN becomes mandatory anyway so may as well secure it upfront.
Applying online at IRS EIN Assistant is free and only takes minutes.
You’ll need to provide your mailing address, ownership structure, and number of employees expected in the next 12 months along with their estimated wages and several other details.
The EIN is generated at the end of the application and also mailed to your business address for records within 2-4 weeks.
With the EIN, remember to register for state taxes in the state where your business is located even if selling apps nationwide. Every state has different rules for sales tax collection or remittance responsibilities. State tax IDs are used for local tax filings.
Stay compliant with federal and state tax requirements from the beginning to avoid any penalties or interest charges as your mobile app startup begins generating revenue.
6. Setup Your Accounting
Proper financial record keeping is crucial for mobile app companies to track revenues and expenses accurately as your business scales.
Accounting Software
Using small business accounting software like QuickBooks automatically imports and categorizes transactions from connected business bank/credit card accounts. This streamlines everything from invoicing to tax preparations.
Integrations with payment gateways also easily record customer app purchases. Dashboards provide real-time insights into cash flow, profits, and loss statements.
Hire an Accountant
While software handles much of the heavy lifting, working with an accountant from the start provides experienced guidance on specialized topics like:
- Setting up payroll, contracts, and payments to any remote developers, designers, or marketing freelancers
- Claiming relevant app development, asset purchase, or online advertising tax deductions
- Sales tax registrations and remittances across states as your customer base expands
- Quarterly/annual tax return filings ensuring full compliance and minimizing IRS audit risk
Expect to budget $200 – $500 monthly for a bookkeeping service and $1000+ for tax preparation filings. Worth the investment for legal protections and optimized savings.
Open a Business Bank Account
Keeping business finances distinct from personal helps tracking and reporting. Open a free small business bank account and apply for a dedicated credit card using your company’s details including the registered business name and EIN.
Apply for a Business Credit Card
Business cards offer higher limits thanks to revenue and asset consideration beyond just a personal credit score. However, you may need to provide financial statements or tax returns to demonstrate company cash flows. Qualifying is easier with an established business history.
7. Obtain Licenses and Permits
Unfortunately, there is insufficient information in your prompt to provide a robust overview of licenses and permits specifically relevant to mobile app businesses. Find federal license information through the U.S. Small Business Administration. The SBA also offers a local search tool for state and city requirements.
The mobile app industry is still an emerging space without consistent regulation across different states and municipalities. However, here are some general considerations around compliance:
Business operations and data infrastructure If functioning only as a software app company without extensive physical business premises or inventory, permits about zoning, health codes, etc may not apply.
Focus compliance efforts instead on data security, privacy, and transparency to build user trust. Adhere to platform policies set by app stores, follow the latest industry best practices around accessible design, and commit to being good data stewards.
Tax registration As covered in previous responses, obtaining a federal EIN and registering for state/local taxes tied to where your business entity is registered/operates is vital to remain compliant right from launch.
Specific vertical apps If building apps in specialized verticals like healthcare, finance, or other highly regulated sectors, additional clearances around personally identifiable information (PII) or sensitive data collection may be needed so do consult attorneys or compliance experts familiar with those spaces.
The tech landscape evolves rapidly so monitor policy updates and changes to ensure your app adheres to the latest legal and ethical obligations users expect.
8. Get Business Insurance
Adequate insurance gives financial protection if unexpected crises threaten operations or trigger large liabilities. Some key policies to consider are:
- General liability insurance: Covers legal claims against accidental bodily harm or property damage caused by your operations. Limits damages paid.
- Professional liability insurance: Protects against claims alleging failure to perform services as promised or breaches of contract.
- Cyber liability insurance: Covers costs associated with data breaches, hacking incidents, or electronic privacy violations.
Not securing relevant policies can have catastrophic implications, for instance:
- User data gets compromised without cyber liability coverage for legal settlements or restoration
- Buggy app triggers major hardware damage for users that general liability has to pay out if sued
- Guaranteed app performance metrics contractual obligations are missed opening professional liability claims
- Founders split makes shareholder agreements complex lacking business insurance guidance
Reaching out to specialized commercial insurance brokers familiar with tech startups is recommended when exploring comprehensive protection.
9. Create an Office Space
Having a professional central workspace even as an app development company lets you host collaborators like remote engineers, conduct user tests, or record videos securely showcasing new features.
Home Office
Converting a spare room into a home office costs little allowing bootstrapped founders to conserve capital for app building initially. Provides flexibility to work odd hours and avoids commutes.
But ensuring fast, reliable connectivity, a comfortable and ergonomic desk setup plus avoiding household distractions take ongoing investment in converting residential spaces into productivity hubs.
Coworking
Space Shared spaces like WeWork offer convenient pay-as-you-go access to office infrastructure from $300 per desk monthly. Utilize conference rooms to coordinate with remote teams or host client meetings as needed rather than getting year-long leases.
Coworking spaces cultivate community, learning opportunities, and networks helping early-stage mobile app entrepreneurs scale knowledge and make connections. Limits privacy for sensitive tasks.
Commercial Office
Leasing’s dedicated office space provides the most control customizing facilities especially to support app demos, events, or operating specialty equipment like video production studios and prototype labs.
But also most expensive at approximately $1500 monthly requiring longer-term commitments. Worth considering once your workforce expands needing extensive customization and private areas for calls, zen rooms, etc.
10. Source Your Equipment
As a predominantly digital business model, mobile app startups need limited physical inventory or materials for core operations beyond office infrastructure.
Focus on reliable computer hardware and productivity software enabling development and collaboration.
Buying New
Order the latest Macbooks, iMacs, or Surface devices for $1000 to handle intensive coding, graphics, and video editing workloads. Optimize specs depending on specialized needs across operating systems with configurable memory, storage, and processors.
Buying Used
Consider 2-3-year-old refurbished devices on eBay saving 50% versus new prices while retaining ample performance for app-building duties. Reliability risks increase with very old equipment. Renting Subscription services like Grover offer short-term rental access to new consoles, drones, VR headsets, etc. for market research or testing innovative app integrations.
Flexible plans depending on duration avoid large upfront investments when experimenting or trying temporary pilot projects.
Leasing
Payment solutions like the Upgrade Program from Apple split costs interest-free over 12-24 months allowing founders to utilize the latest iPhones for $30-50 monthly.
Trade back in before lease-end lets app developers always access modern test devices and preview iOS changes.
11. Establish Your Brand Assets
A consistent visual identity and professional digital properties help new apps appear credible earning user trust. This accelerates organic reach.
Getting a Business Phone Number
Toll-free numbers from providers like RingCentral project an established presence with call routing, voicemail transcriptions, and CRM integrations streamlining customer support as you scale.
Creating a Logo and Brand Assets
A sleek yet meaningful logo encapsulates your vision. Services like Looka offer quick affordable access to designers to create icons, color palettes, and typefaces that balance visual uniqueness with intuitive meaning.
Ensure brand elements guide all experiences customers have through your app, site, emails, and advertising. Familiar branding taps recognition accelerating growth.
Creating Business Cards and Signage
Business card design templates on Vistaprint help craft a cohesive, mobile-friendly identity with custom logos. Cards establish credentials for founder meetings with investors, partners, and media.
Signage can enhance office visits, trade show booths, or offsite pop-up demos showcasing your solution even if not having brick-and-mortar locations long-term.
Purchasing a Domain Name
The right domain name makes your web presence instantly discoverable. Check name availability on Namecheap during registration. Align names to your brand values with logical keywords buyers search for your niche.
Building a Website
Well-designed websites like Wix quickly establish thought leadership and convert visitors into engaged app users with clear messaging and frictionless calls-to-action.
If you lack design experience, specialized Fiverr freelancers provide affordable development support especially as content needs multiply.
12. Join Associations and Groups
Connecting with other local founders and established players in your city’s app ecosystem fosters mutual growth through idea exchanges, partnership opportunities, talent connections, and insight sharing.
Local Associations
Local association groups like the App Association organize frequent learning sessions about the latest iOS changes, UX principles, or scaling on AWS. Attending makes you visible to supportive community connectors opening doors wider than going solo. Carve time for these in-person collisions despite busy builds.
Local Meetups
Market-specific meetups abound on sites like Meetup around mobile gaming, crypto apps, medtech solutions, etc where entrepreneurs unite around shared passions.
Trade shows bring together app talent from designers and hackers to accelerators and angels. The energy is infectious leaving everyone recharged.
Facebook Groups
Thousands connect daily in niche communities like the App Developers Community group finding troubleshooting assistance or team members.
The reach enables access to specialty knowledge that local circles may lack like legal considerations around NFT integrations or spatial computing.
13. How to Market a Mobile App Business
Strategic marketing is imperative for any new app to connect with its initial users and expand visibility leading to organic growth and valuable user feedback for rapid enhancements.
Personal Networking
Tap your trusted circles first enthusiastic evangelists provide social proof helping apps seem credible. Reward referrals via in-app perks. Ask happy users for App Store reviews and testimonials to build credibility.
Digital Marketing
- Start Google/Facebook paid ads targeted using interest/behavioral data and app store optimization for efficient user acquisition
- Produce YouTube tutorials and TikTok videos guiding users through key features
- Guest blog for industry sites linking back to your app store listings
- Run an affiliate marketing program incentivizing external blogs/podcasts to feature your app
- Issue press releases to register on media radars as milestones hit
- Sponsor relevant email newsletters to get visibility among engaged mobile-first users
Traditional Marketing
- Print glossy product brochures for founder meetings with potential investors and partners
- Purchase local radio spots during commute when listeners often discover new apps
- Put up eye-catching about-town posters or placards at bus stops for brand impressions
- Hand out pamphlets and demo invites at busy public places like college campuses
- Run contests awarding cash prizes to incentivize app downloads
Continue testing various options balancing returns tracking conversion rates and cost per acquired user trends across efforts. Double down on the initiatives demonstrating the fastest traction first.
Capitalize on any initial spike through swift product improvements and proactive customer engagement to sustain serial referrals.
14. Focus on the Customer
Delivering empathetic support and promptly resolving issues earns loyal app users who refer others through word-of-mouth, the most trusted endorsement.
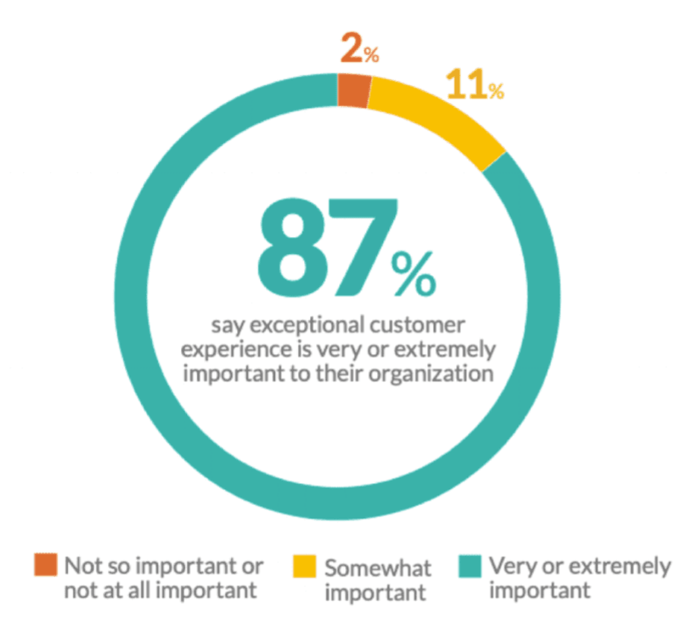
Some ways to improve customer focus in your app development process include:
- Set up multiple channels like in-app chat, email, and social media for reaching support easily. Train agents to personalize interactions using customer data and context from prior conversations.
- Acknowledge receipt immediately when requests come in. If there are complex inquiries, provide expected timelines and progress updates.
- Solve problems completely in one shot instead of handing them off between departments. Follow up proactively checking if further help is needed.
- Make self-serve options like FAQs, forums, and tutorials easily discoverable so for common questions, users have 24/7 access to answers.
- Pay attention to ratings and reviewer commentary across app stores. Categorize feedback into feature requests, bug reports, or experience issues. Set internal benchmarks for response time based on complaint severity.
- Exceed user expectations on support quality because their trust determines ratings and referrals. Pay attention to micro-details like tone, terminology, and resolution timeliness.
Earn gratitude through save offers or exclusive access for loyal long-time users who act as informal brand ambassadors among peers and contribute valuable inputs to shaping your app roadmap.
