The 3D printing industry has experienced rapid growth over the last decade. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global 3D printing market size was valued at USD 13.84 billion in 2021 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 21.0% from 2022 to 2030.
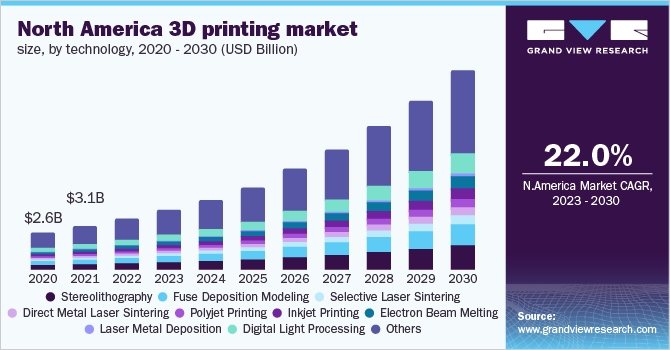
As the technology becomes more accessible and affordable, 3D printing is transforming manufacturing and enabling businesses and consumers to create highly customized products on demand. From prototyping to finished parts production, 3D printing delivers advantages like complexity, customizability, and convenience that make it appealing across diverse industries.
This guide will help you learn how to start a 3D printing business. Topics include market research, sourcing an office and numerous other materials, marketing to attract customers, registering for an EIN, organizing business finances, and more.
1. Conduct 3D Printing Market Research
Market research provides insightful information into building a successful business. 3D printing services offer a new business venture into a wide array of industries, including the medical industry. Many businesses count on market research to identify potential customers and price existing products.
Some information you might learn through market research includes:
- Several factors are driving growth in 3D printing technology and applications.
- 3D printing enables rapid prototyping and cost-effective small-batch production.
- This allows companies to iterate and test designs faster. It also facilitates mass customization of products.
- 3D printing is being adopted across diverse industries like aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and consumer products.
- Advances in materials and printing techniques have expanded capabilities.
- The increased affordability and accessibility of desktop 3D printers have boosted adoption by small businesses, entrepreneurs, and hobbyists.
- The two major 3D printing technologies are stereolithography (SLA) and fused deposition modeling (FDM).
- SLA printers use photopolymers that are cured layer-by-layer by ultraviolet lasers.
- FDM printers extrude thermoplastic filament through a heated nozzle to build objects layer by layer. FDM is slower but printers are more affordable.
Several market segments present opportunities for 3D printing businesses:
- 3D printer sales – Desktop 3D printer sales account for over 60% of total market revenue. As prices drop, demand will grow from small businesses, education sector, and consumers.
- Materials – Photopolymers, thermoplastics like ABS and PLA, metal alloys, and composites are key consumables. Materials sales represent the second-largest revenue share.
- Custom parts manufacturing – Online 3D printing services allow customers to upload designs and get printed parts shipped. This on-demand manufacturing model is gaining traction.
- Software – CAD software, 3D scanners, and design apps complement hardware. Many companies now offer bundled solutions.
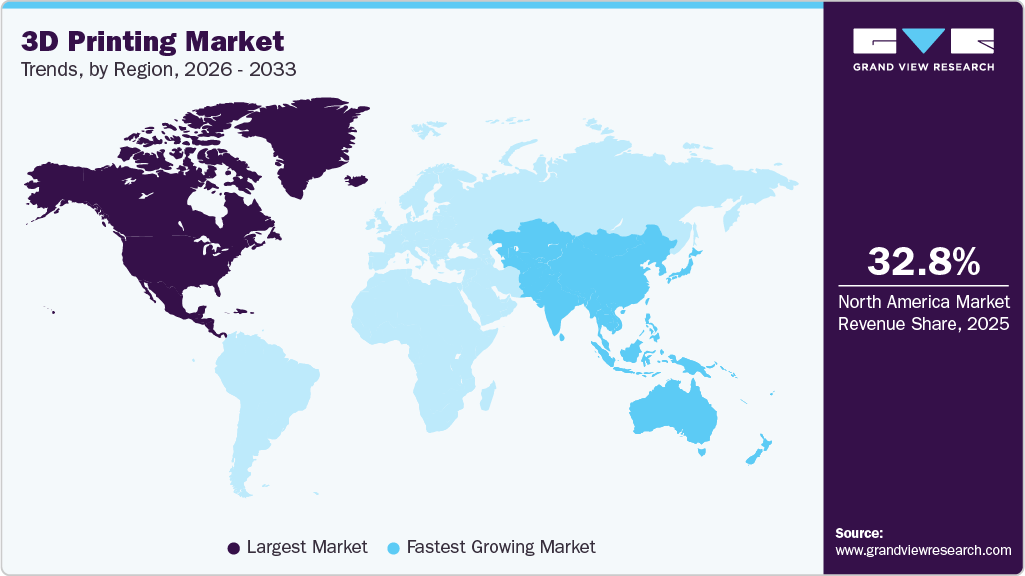
The Asia Pacific region is predicted to be the fastest-growing 3D printing market due to rapid industrialization and investments in manufacturing. North America and Europe are mature markets but still present opportunities in specialty niches.
2. Analyze the Competition
Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for any new business, including in the 3D printing industry. When assessing competition for a potential 3D printing startup, analyze both local brick-and-mortar providers as well as larger online 3D printing services.
Some ways to seek out local competitors include:
- For local competition, search online directories and visit local small business hubs to identify companies offering 3D printing services in your geographic area.
- Analyze their websites and marketing materials to determine their specializations, technologies used, materials offered, and pricing structure.
- Visit their retail locations in person to evaluate customer service, and print quality, and get quotes for sample projects. Check what sort of 3D printing products they offer (e.g. statuettes, cups, mugs, custom designs, etc.)
- Browse their range of printing technologies, materials, and applications to understand their capabilities.
- Upload test designs to get price quotes for comparison.
- Study their website copy, marketing assets, and search rankings to assess their SEO and digital marketing prowess.
- Monitoring their social media engagement can also provide insights into their customer base and brand positioning.
Analyze competitors across criteria including capabilities, technologies, materials, turnaround time, pricing, quality, customer service, and brand reputation. Identify potential gaps or consumer pain points not being addressed effectively.
3. Costs to Start a 3D Printing Business
When launching a 3D printing business, carefully estimating and budgeting for both initial start-up costs as well as ongoing operational expenses is crucial. This will allow you to realistically assess the required capital and run rate to sustain and grow the business.
Start-Up Costs
- Business registration fees – $50-$500 depending on business structure
- 3D printers – For a basic start-up with 1-2 desktop FDM printers, estimate $4,000-$10,000. For higher capacity with industrial SLA printers, budget $60,000-$150,000.
- Materials and supplies – An initial inventory of filament, resins, printer beds, etc. may cost $2,000-$5,000.
- Software – CAD programs, printer operating software, and other design apps can cost $300-$2,000.
- Computer hardware – Desktops or workstations for design and printing, estimate $2,000-$4,000.
- Printer maintenance tools – Calibration kits, nozzles, etc. may cost $500-$1,000.
- Facility – Renting retail/workshop space or buying depending on needs. Budget $2,000-$10,000 for remodels, electrical, etc.
- Marketing – Website development, branding, and signage around $5,000-$10,000 for initial brand establishment.
- Legal/consulting – Lawyers and advisors for contracts, IP, etc. $1,000-$5,000.
- Insurance – Product liability and other coverage $1,000-$5,000.
- Staff – Potentially hiring first employees, estimate $40,000-$80,000 for part-time or full-time staff.
- Working capital – Extra buffer of $10,000-$20,000 for unforeseen expenses.
Ongoing Costs
- Rent and utilities – If leasing space, budget $2,000-$10,000 monthly.
- Salaries – Payroll expenses especially with added staff, estimate $4,000-$15,000 monthly.
- Material costs – Ongoing purchase of printing materials likely $1,000-$5,000 monthly.
- Maintenance – Printer upkeep, parts replacement, around $500-$2,000 monthly.
- Marketing – SEO, Google Ads, trade shows, etc. $2,000-$5,000 monthly.
- Insurance – Yearly premiums $5,000-$20,000.
- Software subscriptions – For design programs, ERP, CRM, estimate $100-$500 monthly.
- Professional services – Accountants, lawyers, and consultants budget $500-$2,000 monthly.
- Miscellaneous – Admin, office supplies, printing, utilities around $500-$1,000 monthly.
Carefully estimating both the upfront investment required, as well as the ongoing overhead enables the creation of a realistic financial plan and secures the capital necessary to start and sustainably grow a 3D printing business.
4. Form a Legal Business Entity
When starting a 3D printing business, choosing the right legal structure is an important decision impacting liability, taxes, and ease of operations. The main options are:
Sole Proprietorship
Simplest structure with no formal registration. The owner has unlimited personal liability for debts and lawsuits. Income is taxed only once personally. Minimal compliance needs but difficult to raise investment capital for growth. Not ideal for a 3D printing business due to product liability risks.
Partnership
Two or more co-owners share control and liability. Income is taxed personally for each partner. Still risky liability for 3D printed products. Allows the pooling of resources but can lack stability if partners disagree.
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
LLCs limit owner liability and combine pass-through taxation with the liability protections of a corporation. Owners have flexibility in the management structure. Easy to add new members/investors. Recommended structure for 3D printing startups as it shields personal assets from lawsuits while allowing business growth. Allows tax-deductible operating losses.
Corporation
Separate legal entity distinct from owners. Owners are only liable up to their investment. Difficult to establish a small 3D printing business and administration is complex. Subject to double taxation on corporate income and dividends. Difficult to attract early-stage investment compared to an LLC.
5. Register Your Business For Taxes
An Employer Identification Number (EIN) is a unique nine-digit number assigned by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to business entities operating in the United States. An EIN is essentially the business equivalent of a social security number and is required for many key business activities.
As soon as you start a business, including a 3D printing startup, you should apply for an EIN even if you do not plan to hire employees. An EIN is required to open business bank accounts, apply for business licenses and permits, file taxes, hire employees later on, and more.
The IRS offers two methods to get your EIN instantly:
Online Application:
- Go to the IRS EIN Assistant: Apply for an EIN Online
- Answer questions about your business structure, activities, and ownership details.
- Provide your personal information such as name, SSN, and address.
- Get your EIN issued immediately after submitting the form.
You can also complete and mail/fax Form SS-4. It takes 4 weeks to receive your EIN compared to instant online.
There is no fee to obtain an EIN. Once received, be sure to register for any required state/local licenses and sales tax permits. With your EIN, you can take key steps to forming and operating your 3D printing business properly and legally.
6. Setup Your Accounting
Proper accounting is crucial for 3D printing businesses to track finances, comply with taxes, and establish credibility. With multiple revenue streams from printer/material sales and custom print orders, clear bookkeeping provides clarity.
Accounting Software
Using small business accounting software like QuickBooks can automate recording income, and expenses, account reconciliation, and generating financial statements. QuickBooks seamlessly integrates with business bank/credit card accounts. For 3D printing businesses, it can track inventory, billable job hours, sales tax calculations, and run profitability reports on your various products and services.
Hire an Accountant
Hiring an accountant provides expertise in recording transactions properly in accounting software, as well as advising on financial strategy and tax compliance. Expect to pay $150-$200 per month for basic bookkeeping and assistance using accounting software up to $1,000 or more monthly for comprehensive financial services.
Open a Business Bank Account and Credit Card
Keeping business and personal finances completely separate is essential. Open a dedicated business checking account and credit card solely for your 3D printing company’s income and expenses. Never co-mingle funds.
For credit cards, business accounts don’t use your credit score but rather the business’ details. Expect lower limits initially but responsible use builds business credit. Apply through your bank or companies like American Express.
7. Obtain Licenses and Permits
Before opening your 3D printing business, be sure to obtain all the necessary licenses and permits. Find federal license requirements through the U.S. Small Business Administration. The SBA also offers state license requirements through its local search tool.
Business License
Most cities and counties require all businesses to register for a general business license, for which fees range from $25 to several hundred dollars annually. This basic permit allows you to legally operate within that jurisdiction.
- Zoning Permits: If you will run your 3D printing business out of a commercial location, confirm the property is properly zoned for manufacturing/retail activities and acquire relevant zoning permits. Expect to pay $100-$500.
- Building Permits: Before any leasehold improvements on a space, you need permits for electrical, HVAC, plumbing, construction, renovations, signage, and more. Building permits help ensure compliance with safety codes and cost around $200-$500 each.
- Fire Safety Permits: If industrial printers/materials are involved, your local fire department may require permits for handling combustible chemicals/gases or operating certain equipment. Expect fees from $50-$150.
- Health Permits: For any food-safe or medical 3D printing, health permits for sanitation may be required. Varies by location but plans for $100-$300 in fees.
- Seller’s Permit: For manufacturing/retail sales, you may need a seller’s or resale permit for tax collection. Fees are usually minimal.
Doing due diligence to get proper certifications before opening your 3D printing business will ensure you operate legally and safely. Depending on your location and activities, work with local Small Business Development Centers to identify requirements.
8. Get Business Insurance
Having adequate business insurance is crucial for a 3D printing startup to mitigate risk. The right policies can protect against potentially company-ending scenarios.
For example, without coverage, a 3D printing business could be financially devastated by:
- A defective 3D printed product that causes injury and prompts a lawsuit.
- A malfunctioning industrial 3D printer that starts a fire damaging your leased facility.
- An employee injury from hazardous equipment opening up workers’ compensation claims.
Properly structured insurance policies transfer these risks to the insurer to keep the business solvent. Key coverages to consider include:
- General liability – Protects against bodily injury, property damage, and product liability claims.
- Commercial property – Safeguards your office, equipment, and inventory from events like fires, theft, and natural disasters.
- Professional liability – Shields against damages from design flaws in 3D printed products.
- Workers’ compensation – Covers medical and lost wage costs for job-related employee injuries.
The typical process for securing business insurance is:
- Research policy options and talk to brokers about your risks.
- Get quotes from providers like The Hartford.
- Purchase required coverage amounts to fully protect your business.
- Provide ongoing documentation at renewal periods.
With proper insurance, your 3D printing business can thrive and grow without fear of financial ruin from the inherent risks.
9. Create an Office Space
Securing an optimal office setup is important for 3D printing companies to conduct sales, production, and shipping efficiently. The right space depends on business activities and budget.
A home office is the most affordable option starting out. Spare rooms work to handle administrative tasks and design files. Meetings with clients can take place virtually or offsite. However, lack of separation between work and home can be challenging. And residential areas may prohibit operating production machinery.
Coworking spaces like WeWork provide affordable flexible offices starting around $300 per month. They offer amenities like meeting rooms, shared equipment, and networking. Coworking is great for the administrative and sales sides but likely not for operating industrial printers.
Renting a small warehouse or retail space provides around 500-1,500 sq ft for $1,000-$3,000 monthly. This accommodates production machinery, inventory, shipping, and a front-office area. An ideal option for active manufacturing and walk-in customers. Signage also boosts local awareness.
Leasing office suites in a commercial building starts around $2,000-$4,000 monthly for 500-1,500 sq ft. More professional than a warehouse but no production space. Best for established brands wanting a branded office presence to meet with clients.
Evaluate your business activities, production levels, customer traffic, and budget. A mix of home office, coworking, and retail production space can optimize cost and capabilities when starting out. As you grow, graduated upgrades to the workspace support scaling efficiently.
10. Source Your Equipment
Launching a 3D printing business requires acquiring key equipment like 3D printers, as well as ongoing printing materials and supplies. Here are the top options for sourcing these startup necessities:
Buying New
For brand-new 3D printers, leading manufacturers include Ultimaker, Formlabs, MakerBot, and Prusa Research. Desktop FDM printers start around $300-$500 for basic models optimal for small jobs. High-precision industrial SLA printers range from $2,000-$6,000.
Buying Used
Significant cost savings can come from purchasing used equipment. Check industry forums like Buy-Sell-Trade as well as eBay, Craigslist, and Facebook Marketplace for deals on pre-owned printers and supplies. Be diligent in inspecting condition and quality before purchasing.
Renting
Renting can be ideal for testing or occasional large production jobs. Online services like 3D Hubs and MakeXYZ allow short-term printer rentals from local owners. Prices range from $10-$150+ per day depending on printer model, materials, and job specifics.
Leasing
Leasing involves lower upfront costs and built-in maintenance/upgrades. Many 3D printer manufacturers like Stratasys and 3D Systems offer operating leases for 12-36 months. Monthly payments are $200-$1,500 depending on equipment capabilities.
11. Establish Your Brand Assets
Developing a strong brand identity is crucial for 3D printing companies to stand out and connect with customers. Carefully crafted visual assets promote recognition and trust.
Getting a Business Phone Number
A professional phone system like RingCentral makes it easy to establish a main business line with call routing, voicemail, etc. This provides a consistent contact number for all marketing.
Creating a Logo and Brand Assets
A logo encapsulates your brand identity. Consider an illustrative logo with graphics relevant to 3D printing that can resonate with tech-savvy customers. Use the logo across your website, signage, packaging, swag, and ads for consistency. Resources like Looka offer affordable DIY logo design.
Business Cards and Signage
Business cards featuring your logo, phone number, and website are essential for networking and sales. Office signage and vehicle wraps containing your brand elements boost local awareness. Order professional, durable cards and signs from Vistaprint.
Purchasing a Domain Name
Your domain name should match your company name and establish your web presence. Use .com over alternate extensions when available. Check name availability with Namecheap and buy for under $20/year.
Building a Website
Every 3D printing business needs a website to showcase products/services and attract leads. Build it yourself with a DIY site builder like Wix or hire a freelancer from Fiverr for customized site development. Make sure your website properly represents your brand.
12. Join Associations and Groups
Joining relevant local and online communities provides invaluable connections when starting a 3D printing business. These groups offer networking, advice, and growth opportunities.
Local Associations
Seek out regional 3D printing and manufacturing trade associations to join. Women in 3D Printing has local chapters supporting female entrepreneurs. Associations give access to seminars, discounts, job boards, and most importantly, networking with like-minded professionals.
Local Meetups
Attending local meetups and trade shows lets you demonstrate products, get feedback, and meet customers and partners. Sites like Meetup list events like maker faires, 3D printing expos, and tech mixers in your area. Bring samples and business cards and actively engage with attendees.
Facebook Groups
Facebook communities bring together 3D printing enthusiasts globally to discuss best practices. Join groups like 3D Printing or Prusa 3D Printing to ask questions and receive support.
13. How to Market a 3D Printing Business
Implementing ongoing marketing is essential for 3D printing companies to gain visibility and attract new customers. A multifaceted approach combining digital promotion, referrals, and select traditional tactics can yield results.

Personal Networking
Satisfied customers providing referrals and word-of-mouth endorsements are hugely impactful. Providing prompt service and premium-quality prints leads to customer loyalty. Consider offering a discount on future orders for any new customer they refer. This incentivizes sharing their great experience.
Digital Marketing
For digital marketing:
- Run Google Ads campaigns targeting those searching for terms like “3D printing services” in your area to drive site traffic.
- Promote beautiful product photos and satisfied customer reviews via social media advertising. Use targeted boosting to reach ideal demographics.
- Create YouTube tutorial videos demonstrating your 3D printing processes to build authority and get discovered.
- Guest blog for 3D printing websites to gain backlinks and position yourself as an expert.
- Send occasional email newsletters with service updates, promotions, and case studies.
Traditional Marketing
For traditional marketing:
- Design eye-catching flyers with service details and distribute them at local retailers, colleges, and community boards.
- Sponsor relevant events like tech conferences and maker fairs to connect with potential customers face-to-face.
- Run radio spots advertising your capabilities and competitive advantages during drive time slots.
- Place signage near high-traffic areas around your location to boost local awareness.
- Send direct mail postcards to businesses that could utilize your services for prototypes or parts production.
The most effective marketing combines select traditional tactics with robust digital activities focused on driving site traffic through relevant content, social media engagement, and paid promotions. Dedicate time and budget monthly to raise awareness and stay top of mind.
14. Focus on the Customer
Providing exceptional customer service needs to be a top priority when starting a 3D printing company. How you support customers directly impacts your referrals, reviews, and repeat business. Some ways to improve customer focus in 3D printing include:
- With 3D printing, customers trust you to accurately produce complex and customized products.
- Great service means communicating timelines, proactively updating customers on order status, and swiftly resolving any issues that arise.
- Going above and beyond on service pays dividends. For example, walk a customer through best practices for getting the most durability from their printed purchase.
- Provide design tweaks for improved printability when you notice an issue with their 3D model file.
- Superior service earns you raving fans.
- Satisfied customers validate you within their networks, generating referrals and word-of-mouth marketing. They leave glowing online reviews that build credibility.
- Alternatively, poor customer service prevents growth.
- Customers frustrated by long delays, lack of communication, or mistakes with their prints will quickly look elsewhere.
For 3D printing startups, devoting resources to customer support provides the best marketing possible. Developing expertise around your niche’s needs, transparent communication, and diligently resolving any problems leads to an army of advocates who help your business thrive.
